AMMOD: Automated Multisensor station for Monitoring Of species Diversity




Research project funded by BMBF
Team: Paul Bodesheim, Dimitri Korsch, Daphne Auer, Julia Böhlke
Time period: 2019 to 2022 (with a one-year extension to 2023)
Joint research project: building weather stations for biodiversity
Climate change is affecting ecosystems all over the world, causing irreversible loss of biodiversity. Since humans are the main contributors to the situation, it is our responsibility to closely monitor the effects of climate change in order to take action for the living beings in our environment in a targeted way. By combining multiple sensors at a single site, we will be able to monitor the whole diversity of flora and fauna in its surrounding, similar to weather stations that record multiple measurements for a local area.
The goal of all AMMOD project partners is therefore to monitor biological diversity in Germany using new technologies. To this end, prototypes for so-called AMMOD stations are to be set up in German forests within the 3-years project period. These are equipped with sensors for recording animal sounds and plant emissions, with animal cameras for birds, mammals and insects, and with automated insect and pollen sample collectors for monitoring by DNA barcoding. These recordings will be used to generate a solid data pool that will enable the analysis of change and possible trends in species richness and populations. For instance, we want to use the detected species to determine their population and record the change over a long period of time.
Find more information on the project homepage (offline as of 2024) of the joint research project. It has been funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung).
Our subprojects for visAMMOD to enable visual monitoring of moths and mammals
The visual monitoring subsystems of AMMOD (visAMMOD) consist of automated insect cameras for collecting images of nocturnal moths, which are called moth scanner, and conventional wildlife camera traps for recording observations of birds and mammals. Experimental stereo camera setups are tested by colleagues from Bonn University.
Our tasks in visAMMOD are the development of algorithms for insect detection and species identification in images provided by the moth scanner, as well as the continuous integration of new camera trap observations in a species identification model, including components for novelty detection, lifelong learning and taxonomic classification.

Moth Scanner
Dimitri Korsch
One camera, the so-called SpeciesMothCam, will take high-resolution images of insects that rest on an illuminated screen at regular intervals. The goal of monitoring is not to detect every species, but to describe trends in local insect populations. Seasonal activity differences of single species, the correlation with weather conditions and with vegetation phenology are important for ecological analyses. The SpeciesMothCam will deliver this type of data. The aim is to implement methods that enable an efficient detection of regions of interest (ROIs) on the screen and a classification of the species in this fine-grained setting. Taxonomic experts will help in the confirmation of the correct identification.
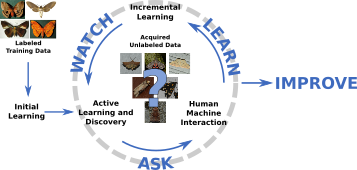
Novelty Detection, Life-long Learning and Classification
Daphne Auer, Julia Böhlke
Another camera, the so-called SpeciesSiteCam, will capture stereo images and videos mainly of terrestrial animals (mammals) using motion sensors. To enable image acquisition during night and twilight, infrared illumination is switched on. Our goal is to build robust classification models that can identify different species. Since there are only a few annotated training image databases, one goal is to compile a first workable system that exploits the image data present in the World Wide Web. Julia Böhlke has written her Bachelor thesis on this topic which is also summarized in a paper. Active learning will play an important role to integrate unlabeled sample sets. Furthermore, a core element of AMMOD is novelty detection, an alerting mechanism in case that a so far unknown species has been recorded by the monitoring devices.
Publications
Automated Visual Monitoring of Nocturnal Insects with Light-based Camera Traps.
CVPR Workshop on Fine-grained Visual Classification (CVPR-WS). 2022.
[bibtex] [pdf] [web] [code] [abstract]
Towards a multisensor station for automated biodiversity monitoring.
Basic and Applied Ecology. 59 : pp. 105-138. 2022.
[bibtex] [pdf] [web] [doi] [abstract]
Automated Visual Large Scale Monitoring of Faunal Biodiversity.
Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis. Advances in Mathematical Theory and Applications (PRIA). 31 (3) : pp. 477-488. 2021.
[bibtex] [pdf] [web] [doi] [abstract]
Minimizing the Annotation Effort for Detecting Wildlife in Camera Trap Images with Active Learning.
Computer Science for Biodiversity Workshop (CS4Biodiversity), INFORMATIK 2021. Pages 547-564. 2021.
[bibtex] [pdf] [doi] [abstract]
Deep Learning Pipeline for Automated Visual Moth Monitoring: Insect Localization and Species Classification.
INFORMATIK 2021, Computer Science for Biodiversity Workshop (CS4Biodiversity). Pages 443-460. 2021.
[bibtex] [pdf] [web] [doi] [code] [abstract]
Exploiting Web Images for Moth Species Classification.
Computer Science for Biodiversity Workshop (CS4Biodiversity), INFORMATIK 2021. Pages 481-498. 2021.
[bibtex] [pdf] [web] [doi] [abstract]
Lightweight Filtering of Noisy Web Data: Augmenting Fine-grained Datasets with Selected Internet Images.
International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP). Pages 466-477. 2021.
[bibtex] [pdf] [web] [doi] [abstract]
